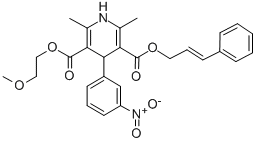
| CILNIDIPINE |
|
| (CAS 132203-70-4) |
 |
| Description: |
Cilnidipine(FRC8653) is a dual L- and N-type calcium channel blocker and displays antihypertensive, sympatholytic and neuroprotective activity.
IC50 value:
Target: calcium channel
Cilnidipine has displayed renal and vascular protective effects and improved baroreflex sensitivity in patients with hypertension. It has also demonstrated neuroprotective effects in a rat focal brain ischemia model by removing free radicals and activating the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathway.
|
| Product No. |
KT20832 |
| Product Name |
CILNIDIPINE |
| Synonyms |
|
| Formal Name |
|
| CAS Number |
132203-70-4 |
| Molecular Formula |
C27H28N2O7 |
| Formula Weight |
492.52 |
| Formulation |
A crystalline solid |
| Purity |
98%min |
| Stability |
2 years |
| Storage |
-20°C |
| Shipping |
USD45 for Europe and USA. No shipping charge once amount reach USD500 |
| Quality Control |
HNMR,CNMR,LCMS,HPLC,IR,etc. |
| Price & Availability |
In Stock. Price Negotiated. |
|
| Related Products: |
Acetylcholine chloride
Acetylcholine is a neurotransmitter that can induce the opening of calcium channels.
Target: Calcium Channel; nAChR; mAChR
Acetylcholine in vertebrates is the major transmitter at neuromuscular junctions, autonomic ganglia, parasympathetic effector junctions, a subset of sympathetic effector junctions, and at many sites in the central nervous system. It is generally not used as an administered drug because it is broken down very rapidly by cholinesterases, but it is useful in some ophthalmological applications.
Acetylcholine chloride, more commonly referred to as just acetylcholine, is a cholinergic neurotransmitter that can induce the opening of calcium channels, as well as act on nicotinic and muscarinic acetylcholine receptors. Acetylcholine plays an important role at many sites in the central nervous system. The compound has been shown to have ophthalmological uses and can be broken down quickly by choliesterases. Studies show that non-neuronal acetylcholine influences many basic cells functions, such as mitosis, cells differentiation, cytoskeletal organization, and cell to cell contact, among other functions [1-3].
|
|


