| Artemisinin |
|
| (CAS 63968-64-9) |
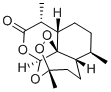 |
| Description: |
Artemisinin (NSC 369397), a widely used anti-malarial drug, is an inhibitor of HCV subgenomic replicon replication.
Target: HCV
Artemisinin (ART), a widely used anti-malarial drug, is an inhibitor of in vitro HCV subgenomic replicon replication. The compound is isolated from the plant Artemisia annua, a herb described in Chinese traditional medicine, though it is usually chemically modified and combined with other medications, as well as being a topic of research in cancer treatment[1].
Treatment with 1?mM artemisinin for 72?h significantly reduced the expression of proliferating cell nuclear antigen messenger RNA. On the other hand, the same treatment increased the apoptosis of VSMCs, the activation of caspase-3, the Bax protein expression, and the Bax/Bcl2 ratio [2].
Clinical indications: Plasmodium falciparum malaria
FDA Approved Date:
Toxicity: nausea; vomiting; anorexia; dizziness.
|
| Product No. |
KT20703 |
| Product Name |
Artemisinin |
| Synonyms |
|
| Formal Name |
|
| CAS Number |
63968-64-9 |
| Molecular Formula |
C15H22O5 |
| Formula Weight |
282.33 |
| Formulation |
A crystalline solid |
| Purity |
98%min |
| Stability |
2 years |
| Storage |
-20°C |
| Shipping |
USD45 for Europe and USA. No shipping charge once amount reach USD500 |
| Quality Control |
HNMR,CNMR,LCMS,HPLC,IR,etc. |
| Price & Availability |
In Stock. Price Negotiated. |
|
| Related Products: |
ABT-333 ABT-333 is an NS5B non-nucleoside polymerase inhibitor.
IC50 value:
Target: HCV NS5B
in vitro:
in vivo: All patients received ABT-333 (400 mg twice daily) and ribavirin (1000 to 1200 mg per day) and one of two daily doses of ABT-450/r. Groups 1 and 2 included previously untreated patients; group 1 received 250 mg of ABT-450 and 100 mg of ritonavir, and group 2 received 150 mg and 100 mg, respectively. Group 3, which included patients who had had a null or partial response to previous therapy with peginterferon and ribavirin, received daily doses of 150 mg of ABT-450 and 100 mg of ritonavir [1]. An interferon-free combination of the protease inhibitor ABT-450 with ritonavir (ABT-450/r), the nonnucleoside polymerase inhibitor ABT-333, and ribavirin showed efficacy against the hepatitis C virus (HCV) in a pilot study involving patients with HCV genotype 1 infection [2].
|
|


