| Adenine;6-Aminopurine;VitaminB4;VitaminB4;6-Aminopurine |
|
| (CAS 73-24-5) |
 |
| Description: |
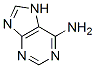
Adenine is a purine derivative and a nucleobase with a variety of roles in biochemistry.
Target: Nucleoside antimetabolite/analog
Adenine is a nucleobase with a variety of roles in biochemistry including cellular respiration, in the form of both the energy-rich adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and the cofactors nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) and flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD), andprotein synthesis, as a chemical component of DNA and RNA. The shape of adenine is complementary to either thymine in DNA or uracil in RNA.
In older literature, adenine was sometimes called Vitamin B4. It is no longer considered a true vitamin or part of the Vitamin B complex. However, two B vitamins, niacin and riboflavin, bind with adenine to form the essential cofactors nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) and flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD), respectively. Hermann Emil Fischer was one of the early scientists to study adenine. Experiments performed in 1961 by Joan Oró have shown that a large quantity of adenine can be synthesized from the polymerization of ammonia with fivehydrogen cyanide (HCN) molecules in aqueous solution, whether this has implications for the origin of life on Earth is under debate
|
| Product No. |
KT20645 |
| Product Name |
Adenine;6-Aminopurine;VitaminB4;VitaminB4;6-Aminopurine |
| Synonyms |
|
| Formal Name |
|
| CAS Number |
73-24-5 |
| Molecular Formula |
C5H5N5 |
| Formula Weight |
135.13 |
| Formulation |
A crystalline solid |
| Purity |
98%min |
| Stability |
2 years |
| Storage |
-20°C |
| Shipping |
USD45 for Europe and USA. No shipping charge once amount reach USD500 |
| Quality Control |
HNMR,CNMR,LCMS,HPLC,IR,etc. |
| Price & Availability |
In Stock. Price Negotiated. |
|
| Related Products: |
5-Azacytidine 5-Azacitidine(5-AzaC) is a nucleoside analogue of cytidine that specifically inhibits DNA methylation by trapping DNA methyltransferases.
IC50 Value: Azacitidine inhibits the L1210 cells growth with IC50 and of 0.019 μg/mL.
Target: DNMT
in vitro: Azacitidine is widely used to demonstrate the correlation between loss of methylation in specifc gene regions and activation of the associated genes. After incorporation into DNA, Azacitidine inhibits DNA methyltransferase noncompetitively, causing a block in cytosine methylation in newly replicated DNA but not in resting, nondividing cells[1]. Azacitidine induces differentiation of Friend Erythroleukemia Cell C3H10T1/2 with myotube formation[2]. Azacitidine can be activated to the nucleoside triphosphate and incorporate into both DNA and RNA, leading to inhibition of DNA, RNA and protein synthesis in normal eukaryotic cells and in cancer cell lines, which could finally leads to cell death. Azacitidine also inhibits the incorporation of purine metabolites into macromolecules. Azacitidine inhibits the L1210 cells growth with IC50 and of 0.019 μg/mL[3] .
in vivo: Azacitidine inhibits polynucleotide synthesis in leukemic BDF1 mice[3] . Azacitidine (3 mg/kg, i.p.) increases the mean survival time in leukemic BDF1 mice inoculated with Ll210 ascites tumor cells. Azacitidine markedly suppresses all enzymes activity in the polyamine-biosynthetic pathway, including ornithine decarboxylase activity. putrescine-dependent S-adenosyl-L-methionine decarboxylase activity, and spermidine-dependent S-adenosyl-L-methionine decarboxylase activity. Azacitidine also inhibits the accumulations of polyamines in leukemic mice[4].
Clinical trail: A Phase III study to the Azacitidine on clinically significant adverse cardiovascular and cerebrovascular events in high-risk subjects undergoing coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery has been completed
|
|


