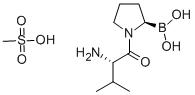
| [(2R)-1-[(2S)-2-Amino-3-methylbutanoyl]pyrrolidin-2-yl]boronicacidmesylate |
|
| (CAS 150080-09-4) |
 |
| Description: |
Talabostat mesilate(PT-100; Val-boroPro) is an orally active, specific inhibitor of dipeptidyl peptidases(IC50=1 nM for DPP4), including tumor-associated fibroblast activation protein.
IC50 value: 1 nM [1]
Tareget: DPP4
By cleaving N-terminal Xaa-Pro or Xaa-Ala residues, talabostat inhibits dipeptidyl peptidases, such as fibroblast activation protein (FAP), resulting in the stimulation of cytokine and chemokine production and specific T-cell immunity and T-cell- dependent activity. This agent may also stimulate the production of colony stimulating factors, such as granulocyte colony stimulating factor (G-CSF), resulting in the stimulation of hematopoiesis. Dipeptidyl peptidases are involved in the activation of polypeptide hormones and chemokines.
|
| Product No. |
KT20605 |
| Product Name |
[(2R)-1-[(2S)-2-Amino-3-methylbutanoyl]pyrrolidin-2-yl]boronicacidmesylate |
| Synonyms |
|
| Formal Name |
|
| CAS Number |
150080-09-4 |
| Molecular Formula |
C10H23BN2O6S |
| Formula Weight |
310.17 |
| Formulation |
A crystalline solid |
| Purity |
98%min |
| Stability |
2 years |
| Storage |
-20°C |
| Shipping |
USD45 for Europe and USA. No shipping charge once amount reach USD500 |
| Quality Control |
HNMR,CNMR,LCMS,HPLC,IR,etc. |
| Price & Availability |
In Stock. Price Negotiated. |
|
| Related Products: |
Alogliptin Alogliptin(SYR-322) is a potent, selective inhibitor of DPP-4 with IC50 of <10 nM, exhibits greater than 10,000-fold selectivity over DPP-8 and DPP-9.
IC50 value: <10 nM
Target: DPP4
Alogliptin is an orally administered, anti-diabetic drug in the DPP-4 inhibitor class. A randomized clinical trial reporting in 2011 aimed to determine the efficacy and safety of alogliptin versus placebo and voglibose among newly diagnosed Type 2 diabetes patients in Japan. The main outcome indicated that alogliptin was statistically superior to both comparitors. A randomized clinical trial reporting in 2012 aimed to demonstrate that alogliptin was "non-inferior" to a "very low fat/calorie traditional Japanese diet" among newly diagnosed Type 2 diabetes patients in Japan. The outcome indicated that both the drug and dietary treatments comparably impacted indicators of the diabetic condition, such as HbA1c levels and glycemic efficacy. The drug treatment had its impact without changing body mass index (BMI), but the dietary treatment was accompanied by a significant reduction in the BMI…
|
|


